Understanding Cloud and Cloud Computing Basics
Uncover cloud and cloud computing fundamentals. Explore self-service, elasticity, IaaS, PaaS, SaaS, and deployment types for growth. Click now!

We understand that handling the demands of digital transformation can be challenging, especially when daily operations and limited IT resources already strain your team.
As technology continues to evolve, cloud computing has become a vital tool. It offers businesses the flexibility, scalability, and cost-efficiency needed to adapt and grow. In 2024, 94% of UK enterprises are utilising some form of cloud service, underscoring its growing importance across various industries.
From manufacturing and finance to education, professional services, and non-profits, understanding the cloud is critical for staying competitive and driving long-term success. In this blog, we’ll explore the fundamentals of cloud computing, its core service models and deployment options, and how it helps organisations overcome key challenges in today’s business environment.
What is Cloud Computing?
Cloud computing refers to the delivery of computing services, including storage, processing power, databases, networking, and software, over the internet. Rather than relying on local servers or personal computers, cloud computing enables businesses to access resources on demand from third-party providers.
The cloud computing sector is rapidly growing, with a turnover of £29.8 billion and £1.2 billion in investment, expanding at 22.1% annually. This growth supports its versatile application across industries, helping companies modernise legacy systems, streamline operations, and securely manage data.
- Business Benefits:
- Eliminates the need for expensive hardware and on-site infrastructure
- Offers a cost-efficient, scalable, and flexible solution
- Reduces capital expenditure and IT maintenance burden
- Industry Applications:
- Used across a wide range of industries
- Helps modernise legacy systems
- Supports workflow integration and secure data management
Traditional IT Setups vs. Cloud Computing
Traditional IT setups and cloud computing represent two different approaches to managing and delivering technology services. The table below highlights the key differences between these models in terms of cost, flexibility, and operational efficiency.
| Aspect | Traditional IT Setups | Cloud Computing |
| Infrastructure | Requires on-site servers and hardware with high upfront costs. | Uses remote data centres with no need for local hardware. |
| Scalability | Scaling requires purchasing and installing new equipment. | Instantly scalable based on demand. |
| Accessibility | Access is limited to physical location or VPN setups. | Accessible from anywhere with an internet connection. |
| Maintenance & Updates | IT staff must manage hardware, updates, and backups manually. | Managed by cloud providers with automated updates and backups. |
| Cost Model | Capital-intensive with ongoing maintenance costs. | Pay-as-you-go model reduces upfront costs and allows better cost control. |
Key Characteristics of Cloud Computing
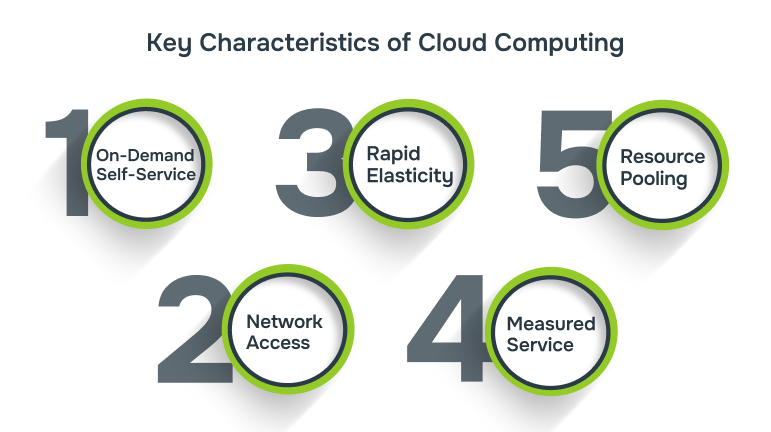
Cloud computing has several defining characteristics that make it an attractive choice for businesses:
1. On-Demand Self-Service
Cloud computing allows users to provision computing resources such as server time and network storage automatically and on demand, without needing to contact the service provider. Customers can use a web-based self-service portal to access their cloud accounts, monitor usage, and easily add or remove services as needed.
2. Broad Network Access
Cloud services can be accessed over the internet or a network from a wide range of devices, including smartphones, tablets, laptops, and desktop computers. Public clouds operate over the internet, while private clouds use internal networks such as local area networks (LANs). The performance of these services is heavily influenced by latency and bandwidth, which impact the speed, responsiveness, and overall quality of the user experience.
3. Rapid Elasticity
Cloud services offer rapid elasticity, allowing resources to be provisioned and released as needed, often automatically. This enables customers to scale up or down quickly based on demand. The available resources for provisioning are virtually unlimited, and users can access them at any time in any quantity. Cloud usage, capacity, and cost can be adjusted without the need for additional contracts or fees. Instead of purchasing physical hardware, customers can rely on the cloud provider’s computing resources.
4. Measured Service
Cloud systems use metering capabilities to track and optimise resource usage at a level suitable for each type of service. Services such as storage, processing, bandwidth, and user access can be measured and billed based on actual consumption. This pay-as-you-go model ensures customers only pay for what they use. Monitoring, controlling, and reporting resource usage helps create a transparent and efficient experience for both service providers and consumers.
5. Resource Pooling
Resource pooling enables multiple customers to share physical and virtual resources through a multi-tenant model. In this setup, resources are dynamically assigned and reassigned based on demand. Multi-tenancy allows users to share infrastructure or applications while maintaining privacy and security. While customers may not know the precise location of their resources, they can often choose a general location, such as a specific country, region, or data center. Commonly pooled resources include memory, processing power, and bandwidth.
Types of Cloud Computing Service Models
Cloud computing services are typically divided into five main models, each offering a distinct level of control and responsibility.
| Model | Description | Examples | Advantages | Disadvantages |
| SaaS (Software as a Service) | Use software over the internet without installing or managing it. | Google Docs, Dropbox, Salesforce, Office 365 | – No installation- Accessible anywhere- Automatic updates- Pay-as-you-go | – Limited customisation- Internet dependent- Data privacy concerns |
| PaaS (Platform as a Service) | Provides a ready-to-use platform for app development without managing the backend. | AWS Elastic Beanstalk, Google App Engine, Azure | – No hardware setup- Faster development- Built-in tools | – Less infrastructure control- Provider lock-in- Limited workload support |
| IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service) | Rent virtual hardware like servers and storage from a provider. | AWS, IBM Cloud, OpenStack, VMware, Rackspace | – Scalable- Cost-effective- Full control over apps | – Security setup is user’s job- Less control over infrastructure |
| XaaS (Anything as a Service) | Combines multiple services (SaaS, PaaS, IaaS) and more into one flexible model. | Salesforce, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud Suite | – Flexible & scalable-Customisable services- Cost savings | – Integration challenges- Limited flexibility for unique workloads |
| FaaS (Function as a Service) | Run code snippets in response to events without managing servers. | AWS Lambda, Google Cloud Functions, OpenFaaS | – Pay per use- Scales automatically- No server management | – Cold start delays – Limited control – Not ideal for heavy traffic |
Deployment Models in Cloud Computing
Cloud computing can be deployed in various ways depending on the needs and preferences of a business. The main deployment models include:
| Deployment Model | Description | Advantages | Examples |
| Public Cloud | Operated by third-party providers and shared among multiple organisations via the internet. | – Scalable – Cost-effective – High availability – Accessible globally | AWS, Microsoft Azure, Google Cloud |
| Private Cloud | Dedicated to a single organisation; hosted on-premises or by a third-party. | – High security – Customisation – Regulatory compliance- Privacy | HP Data Centers, Ubuntu Private Cloud |
| Community Cloud | Shared among organisations with similar needs/interests; managed internally or by a provider. | – Cost-sharing- Collaboration- More secure than public- Scalable | Government or healthcare collaborations |
| Hybrid Cloud | Combines public and private clouds to balance scalability, control, and security. | – Flexibility- Cost efficiency- Scalable- Strong disaster recovery | AWS Outpost, Google Anthos, Azure Stack, Oracle Cloud at Customer |
Key Benefits of Cloud Computing

Cloud computing offers numerous advantages for businesses, including:
- Cost Efficiency: Cloud services eliminate the need for expensive hardware, reduce maintenance costs, and allow for pay-as-you-go pricing models, which are especially beneficial for organisations with fluctuating workloads.
- Scalability: Cloud platforms provide businesses with the flexibility to scale their infrastructure up or down based on demand. This ensures that businesses can respond quickly to changes in the market without the burden of over-investing in resources.
- Improves Collaboration: Cloud computing enables seamless collaboration across teams, departments, and locations. With cloud-based tools like Microsoft Teams or SharePoint, employees can access documents, share information, and work together in real time, enhancing productivity and communication.
- Business Continuity: Cloud services come with built-in redundancy and backup options, ensuring that your critical data and systems are protected and easily recoverable in case of a disaster.
- Security: Reputable cloud providers implement advanced security measures, including encryption, firewalls, and multi-factor authentication, to ensure that your data is safe from cyber threats.
Common Use Cases of Cloud Computing
Cloud computing has a wide range of use cases across various sectors. Here are some common examples:
- Cloud-Based CRM and ERP: Cloud services such as Microsoft Dynamics 365 can be used by manufacturing companies, professional services firms, and finance institutions to manage customer relationships, automate processes, and ensure compliance.
- Data Storage and Backup: Cloud solutions provide secure and scalable storage for organisations of all sizes. Cloud-based backup services ensure that your data is safely stored and recoverable in the event of data loss or cyberattacks.
- Remote Work Solutions: As more organisations adopt hybrid or remote work models, cloud-based tools like Microsoft 365 and Google Workspace provide essential services, including communication, document sharing, and project management.
- Cloud Analytics: By using cloud platforms like Azure, businesses can gather, analyse, and visualise data in real time, helping them make more informed decisions and improve operational efficiency.
How Alberon Supports Your Cloud Transformation?
At Alberon, we understand that embracing cloud computing is not just a technological decision; it’s a strategic one. That’s why we offer tailored cloud solutions designed to meet the unique needs of your organisation, whether you’re just beginning your cloud journey or looking to optimise an existing setup.
Our Services Include:
- Secure Cloud Migration & Hosting: We ensure a smooth, secure, and minimally disruptive transition to the cloud. Protecting your data every step of the way.
- Security & Compliance: We implement best-in-class security measures and ensure your cloud environment meets industry standards and regulations.
- Scalable Infrastructure for Business Growth: We build flexible cloud environments that scale with your business, enabling you to respond to changing demands without overinvesting in resources.
- Cloud-Based Data Storage & Management: Our solutions provide reliable, centralised, and compliant data storage, making it easier to access, manage, and protect your critical business information.
- Support & Training: We provide expert support and training to empower your team and ensure long-term success in the cloud.
- Microsoft Product Training – Tailored sessions to help your team get the most out of tools like Microsoft 365, SharePoint, and Microsoft Dynamics.
At Alberon, we provide expert support and hands-on training to empower your team and ensure long-term success in the cloud.
Conclusion
Cloud computing is no longer a futuristic concept; it’s a business imperative. As digital transformation accelerates across every sector, cloud services offer the agility, efficiency, and resilience organisations need to remain competitive and future-ready.
Whether you’re looking to modernise legacy systems, support a remote workforce, or enhance data security and compliance, cloud computing provides the tools to scale and innovate with confidence.
Contact us todayto explore how our cloud services can drive growth and efficiency for your organisation.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What’s the difference between the cloud and cloud computing?
The cloud refers to remote servers and data centres that store and manage data online. Cloud computing, on the other hand, is the broader concept of delivering computing services, like servers, storage, software, and databases, over the internet. In short, the cloud is the infrastructure, while cloud computing is how that infrastructure is used.
2. How is cloud storage different from cloud computing?
Cloud storage is a service that lets you save and access files, documents, and backups online. Cloud computing goes further by allowing you not only to store data but also to process, manage, and analyse it using remote servers. If you just need extra space to store files, cloud storage is ideal. If you want to run applications, analyse data, or host websites, cloud computing is a better choice.
3. What does “the cloud” mean?
The cloud refers to a network of remote servers accessed over the internet that store, manage, and process data. It allows users and businesses to run applications, store files, and use services like databases and networking tools—anytime, from anywhere with an internet connection.
4. Do you need coding skills for cloud computing?
Not always. Many cloud-related roles, like cloud support specialists or system administrators, focus on managing and configuring services, which may not require coding. However, for more technical roles like cloud developers, DevOps engineers, or those working with infrastructure as code (IaC), programming knowledge is essential.
Get in Touch Today:
Ready to Improve your Business Productivity
Get a trusted partner to navigate your digital transformation. With Alberon, you can ensure a smooth transition, clear communication, and peace of mind.
